Theme: “New Frontiers in Biosimilars Biologicsâ€
Biosimilars-2022
- About Conference
- Sessions and Tracks
- Market Analysis
- Abstract Submission Criteria and Eligibility
- Participation Options and Benefits
The "5th Annual Congress on Biosimilar on September 28-29, 2022" is becoming an unmissable meeting where Biosimilar partners are accumulating to address the current and future state of Biosimilar in Rome,Italy.
The expansion of two dedicated strands to the Biosimilar Congress meeting was a success - we were able to gather insights from two particular groups - one that exceeded expectations on the systematic and assembly side - and the another that exceeded expectations on the commercial and key side.
Setting up this meeting in 2022 will allow us to continue to dig deeper into both the investigation of improving biosimilars.
The Organizing Committee is delighted to invite you to attend the 5th Annual Congress on Biosimilar, one of its outstanding Biotechnology conferences, to be held on, September 28-29, 2022 in Rome, Italy. The 5th Annual Congress on Biosimilars is an annual global event. This Biosimilars Congress 2022 will bring together scientists, researchers, business development managers, CEOs, directors, IP lawyers, regulators and CROs from around the world. Many biologics are entering the Biotechnology market and experiencing a noticeable increase in their use compared to conventional drugs.
At Biosimilars 2022, meet your target audiences from around the world focused on learning about biologics and Biosimilar. This conference would be your best opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of participants from the biologics and Biosimilar community.
2022 Highlights:
300+ Participation (70 Industry: 30 Academia)
10+ keynote speakers
50+ plenary speakers
20+ exhibitors
14 innovative educational sessions
5+ workshops
B2B meetings
Track 1: Biosimilars
A biosimilar product is an FDA-approved biologic product that has been shown to be remarkably similar to another FDA-approved biologic product, also known as a reference product, and to differ from the reference product in neither safety nor efficacy in any clinically relevant ways. Biosimilar goods can only have very small variations in therapeutically inactive components. In terms of safety, purity, and potency, biosimilars are quite comparable to the reference product, however there may be small changes components that are clinically inactive. Recombinant DNA technology is used to create biosimilars in live organisms, as opposed to the generic drugs, chemical synthesis is necessary. The production of biosimilars is more difficult than that of conventional small molecules. Generics primarily because biosimilars have bigger, more intricate molecules.
Track 2: Biosimilar in Oncology
Oncology is the study of cancer. An oncologist is a doctor who treats cancer and provides medical care for a person diagnosed with cancer. An oncologist may also be called a cancer specialist. The field of oncology has 3 major areas based on treatments: medical oncology, radiation oncology, and surgical oncology. The primary purpose of biosimilars is to reduce the healthcare costs associated with the use of biologics and thereby increase access to healthcare. Unlike small molecule generics, the bioequivalence approach is not considered appropriate for the approval of biosimilars.
Track 3: Emerging Biosimilars in Therapeutics
The first wave of approved biopharmaceuticals' patents have either already expired or will soon do so. Generic versions, also known as "biosimilars" (European Union) or "follow-on protein products," are now becoming more widely available (United States).To make wise treatment choices, healthcare providers need to be aware of the crucial problems regarding the use of biosimilars. The variety, high-molecular-weight three-dimensional complexity, and manufacturing reliance of biopharmaceuticals in live cells distinguish them from traditional chemical medicines. Current analytical techniques are unable to characterise these complicated adequate to demonstrate structural similarity to reference compounds. Confirmation of biosimilars' resemblance to Innovative biopharmaceuticals continue to be a major obstacle. Additionally, the immunogenicity of biopharmaceuticals, a crucial safety concern, has received attention recently, indicating the necessity
Track 4: Pharma covigilance challenges in Biosimilars
Since 2000, biosimilars have been sold in India. Similar to biologics, biosimilars are made in live organisms and have a huge size, intricate structure, and difficult production procedure. It demands specialist administration equipment and more stringent temperature control to prevent degradation. Because of the shortened development process for biosimilars, adverse incidents (AEs) an unidentified during a clinical trial could be found after marketing. India has seen a considerable rise in pharmacovigilance awareness following the January 2018 implementation of the pharmacovigilance guidance. However, to assure their safety, biologics need more rigorous surveillance efficiency, too. The significance of pharmacovigilance for biosimilars is discussed in this review article along with how it differs from generic vigilance. Proposals for educating doctors and scientists about the need for a new strategy to improve pharmacovigilance. Pharmacovigilance for innovator biologics and biosimilars is equally as vital as for generic drugs.
Track 5: Biological Medicine
Any pharmaceutical therapeutic product created in, extracted from, or partially synthesised from biological sources is referred to as a biopharmaceutical, sometimes known as a biologic medical product or biologic The most cutting-edge medicines now accessible, biologic medications are used to treat a wide range of illnesses and ailments. Rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and other autoimmune illnesses are treated with several biologic medications. Biologics are medicines made from blood, proteins, viruses, or living things. Additionally, they are employed in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of numerous medical disorders.
Examples of typical biologics
- Lantus (insulin glargine)
- Humira (adalimumab),
- Herceptin (trastuzumab),
- Avastin (bevacizumab)
- Botox (onabotulinumtoxinA)
Track 6: Biopharmaceutical Informatics
In Biopharmaceutical Informatics, it is explained how methods from Molecular Biophysics and Information Technology can be successfully applied to the discovery and development of biologic medications. The use of computational techniques and bioinformatics tools to address
problems in the development of biopharmaceutical drugs is known as biopharmaceutical informatics. Creating databases with biophysical data, simulating molecules, and statistically analysing biopharmaceutical datasets are also included. The goal of biopharmaceutical informatics is to encourage the use of computer techniques in the research and development of biologic medicines. When fully implemented, it will allow for quick, materials-free developability assessments of biologic drug candidates at the early stages and streamline tasks like commercial scale production, purification, formulation, analytical characterization, safety, and in vivo performance during the development of drug products.
Track 7: Chemical and Analytical Strategies for Biosimilars
Regulatory agencies require biosimilar goods to be appropriate and equivalent in terms of quality, safety, and efficacy to a reference biologic product. The analytical methods that makers of biosimilar medicines have at their disposal are highly developed and offer a variety of alternatives to characterise the goods and compare them with the pertinent commercially available reference product. The attributes of a candidate biosimilar and a reference biologic can be compared using a variety of analytical techniques, and this ensures that different techniques can be used to characterise different aspects of a single attribute, allowing for thorough structural characterization and physicochemical assesment. With the help of these analytical approaches, a biosimilars developer can incorporate risk reduction into the development strategy in addition to gathering data for bio-comparability. This review talks about the analytical methods that can be used to support comparability testing, the management of reference material, and the commercialization strategy for biosimilar or subsequent biological medicines.
Track 8: Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
The rate and degree to which a substance that is therapeutically active is absorbed from a drug product into the systemic circulation and made available at the site of action is measured by bioavailability. Although generic medications are the subject of most discussions about bioequivalence. An important predictor of drug absorption is bioavailability. It stands for the provided dose fraction that, when given orally or through another extravascular dosing method, successfully reaches the systemic circulation. The quality of two dosage forms or active substances that generate the same effect at the location of physiologic action is known as bioequivalence. Bioavailability is the term used to describe the rate and volume of absorption. The comparison of the bioavailability of two medication formulations is known as bioequivalence.
Track 9: Immunogenicity of Biosimilars
Immunogenicity is the propensity of therapeutic biologics to elicit immune responses to themselves and to related proteins or to trigger undesirable clinical outcomes or immunologically related non-clinical effects. When we think about immunogenicity, we mostly consider very minor tweaks to the manufacturing process, adjustments to the purifying procedure, and potential post-translational alterations. Strategies for evaluating the immunogenicity of biosimilars are developed on a case-by-case basis. The evaluation's goal is to identify potential variations in the frequency and intensity of human immunological responses between the biosimilar candidate and the reference product. Small (indiscernible) changes between biosimilars and the original medications could cause patients to develop unexpected immune responses, which is a big worry.
Track 10: Drug Desiging
Drug design is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the molecular target with which they interact and bind. The Drug Discovery Process involves many different stages and series of actions. Typically, it can be divided into four main stages: Early Drug Discovery, Pre-Clinical Phase, Clinical Phases, and Regulatory Approval.
Track 11: Infliximab
A number of autoimmune illnesses are treated with infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody that goes by the brand name Remicade among others. These conditions comprise Behçet's disease, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis. A biological therapy is a class of medication that includes infliximab. Rheumatoid arthritis may be treated with it. axial spondyloarthritis, such as ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis When other medications have failed to control the symptoms of moderately to severely active Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis in adults and children, infliximab injection is regulated.
Track 12: Goblization of Biosimilar
The primary purpose of biosimilars is to reduce the healthcare costs associated with the use of biologics and thereby increase access to healthcare. Unlike small molecule generics, the bioequivalence approach is not considered appropriate for the approval of biosimilars. Many experts believe that biosimilars are essential to the future of healthcare because they lead to greater competition and innovation in the market, causing prices to drop and allowing greater access to the medication for patients — wherever in the world they may be.
Track 13: interchangeable Biosimilar
An interchangeable biosimilar product may be substituted without the intervention of the health care professional who prescribed the reference product, much like how generic drugs are routinely substituted for brand name drugs. This is commonly called pharmacy-level substitution and is subject to state pharmacy laws. The FDA has approved 2 interchangeable biosimilars—biosimilars that pharmacists could substitute interchangeably with reference drugs—since July 2021, but manufacturer-developers are seeking interchangeable status for about 7 other biosimilars, according to Jeff Casberg, MS, RPh, vice president of Clinical Development .
Track 14: Drug Delivery and Development
A drug delivery system is a formulation or a device that enables the introduction of a therapeutic substance in the body and improves its efficacy and safety by controlling the rate, time and place of release of drugs in the body. Absorption, Distribution, Disposition, Metabolism, & Excretion (ADME) is a Pharmacokinetic (PK) process of measuring the ways the new drug affects the body. ADME involves mathematical descriptions of each effect. Proof of Principle (PoP) are studies that are successful in preclinical trials and early safety testing.
Track15: Clinical Trials of Biosimilars
Clinical trials aim to resolve uncertainties that may remain following nonclinical development regarding the similarity of the proposed biosimilar with the reference product. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies form the backbone of early clinical development and serve to inform phase 3 clinical development. The primary purpose of biosimilars is to reduce the healthcare costs associated with the use of biologics and thereby increase access to healthcare. Unlike small molecule generics, the bioequivalence approach is not considered appropriate for the approval of biosimilars.
Biosimilar: Global Markets 2022
Research Report 2022 provides key analysis on the market status of biologics and biosimilars manufacturers with top facts & figures, meaning, definition, SWOT analysis, expert opinions and latest developments at worldwide. The report also calculates the market size, biologics and biosimilars sales, price, revenue, gross margin and market share, cost structure and growth rate. The report examines the revenue generated and technologies by various application segments and walks through market data tables and figures with in-depth TOC in Biologics and Biosimilars Market.
Impact of COVID-19 on the Biosimilars Market In 2022:
The sudden onset of the COVID-19 pandemic has led to the implementation of strict containment regulations in several countries, which has led to disruptions in the import and export activities of biological products and biosimilars. COVID-19 can affect the global economy in three main ways: by directly affecting production and demand, by creating supply chain and market disruptions, and by its financial impact on businesses and financial markets . Our analysts monitoring the situation around the world explain that the market will generate rewarding prospects for producers after the COVID-19 crisis. The report aims to provide an additional illustration of the latest scenario, economic downturn and the impact of COVID-19 on the overall industry.
The key Players in the Biosimilars market:
â— Roche
â— Amgen
â— AbbVie
â— Sanofi-Aventis
â— Johnson and Johnson
â— Pfizer
â— Novo Nordisk
â— Eli Lilly
â— Novartis
â— Merck
â— 3sbio
â— Changchun High Tech
â— CP Guojian
â— Biotech
â— Gelgen
â— Innovent
â— Dong Bao
â— Ganlee
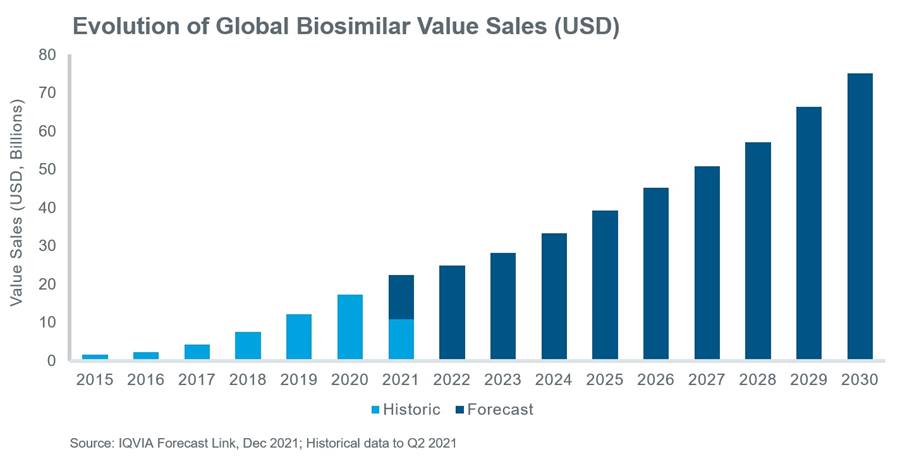
Scope Of the Biosimilars Market:
The Global Biologics and Biosimilars market size is projected to reach USD 313530 million by 2026, from USD 240760 million in 2020, at a CAGR of 4.5% during 2021-2026.
Global Biologics and Biosimilars Market Segment:
The global biosimilars market is segmented by company, region (country), by type and by application. Players, stakeholders, and other participants in the global Biologics and Biosimilars market could gain the upper hand as they use the report as a powerful resource. The industry analysis focuses on revenue and companies by region (country), by type and by application for the period 2015-2026.
Abstract Submission Criteria and Eligibility
Participating authors are answerable for registration, travel, and hotel costs. Note: Those with submitted abstracts will get an acknowledgment mail enabling them to enroll for the gathering.
Abstracts will be compiled, and conference books are made available to participants at the conference.
Any presenter who is unable to attend should arrange for another qualified individual to present the paper/poster in question. If such a change is necessary, please notify our conference team
Oral paper introductions will have 30-minute schedule time slot. The keynote session will have for 45-minute presentation duration, workshop/special session will have 1-hour long schedule opening and symposium will have 1-hour long availability followed by 5-minute Q&A session.
Graduate and master’s understudies are qualified to present their abstracts under poster and e-poster presentation category.
Ph.D. understudies are qualified to submit their abstract under special YRF (Young Researcher's Forum), poster and e-poster presentation category.
NOTE: YRF category includes short oral presentation especially for Ph. D. students
Extended abstract: Submissions should utilize the Abstract Template. Papers submitted in this category may represent original empirical research, theoretical development, reviews, or critiques.
Physiotherapy Conference provides the participants with different modes or ways to participate such as Delegate or Speaker under either ACADEMIC / STUDENT / BUSINESS Category. Mode of participation is Online through Power Point Presentation/ Video Presentation on Cisco Webinars.
Keynote speaker: 45-50 minutes
Speaker (oral presentation): 25-30 minutes (only one person can present)
Speaker (workshop): 45-50 minutes (more than 1 can present)
Speaker (special session): 45-50 minutes (more than 1 can present)
Speaker (symposium): more than 45 minutes (more than 1 can present)
Delegate(only registration): will have access to all the sessions with all the benefits of registration
Poster presenter: can present a poster and enjoy the benefits of delegate
Remote attendance: can participate via video presentation or e-poster presentation
Exhibitor: can exhibit his/her company’s products by booking exhibitor booths of different sizes
Media partner
Sponsor
Collaborator
For more details about each mode, kindly contact: https://biosimilars.conferenceseries.com/
Benefits of Joining Conference:
Get your abstract published with DOI
Get certified for your participation
Reduced Costs Affordability
Knock Down Geographical Barriers
Convenience from comfort of your own home or from work
They’re Archived: Ability to view events in the recording
Great resource for learning new career skills
Learn from the Pros
Global exposure to your research
Make new connections
Significant time saving
Increased engagement
Wider Reach
More Engaging
Position yourself as the expert
Get your abstracts published with unique DOI in International Journals
Get up to 50% discounts for publishing your entire article in our open access International Journals
Get Handbooks and conference kits
Get an access to the network with eminent personalities from worldwide.
Conference Highlights
- Biosimilars
- Biosimilars In Oncology
- Emerging Biosimilars in Therapeutics
- Pharma covigilance challenges in Biosimilars
- Biological Medicine
- Biopharmaceutical Informatics
- Chemical and Analytical Strategies for Biosimilars
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Immunogenicity of Biosimilars
- Drug Designing
- Globalization Of Biosimilars
- interchangeable Biosimilar
- Immunogenicity
- Drug Delivery and Development
- Clinical Trials of Biosimilars
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | September 28-29, 2022 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by












